Consonant Sounds
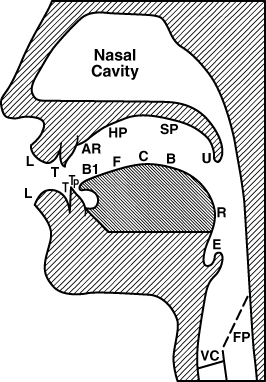
The other class of speech sounds is consonants. In pronouncing consonants, there is audible frictional noise made by the organs of speech. “ A consonant is a speech sound produced by a complete or partial stoppage of the breath.
The way of producing consonants is characterized mainly by some obstruction above the larynx, especially in the mouth cavity.
The other class of speech sounds is consonants. In pronouncing consonants, there is audible frictional noise made by the organs of speech. “ A consonant is a speech sound produced by a complete or partial stoppage of the breath.
The way of producing consonants is characterized mainly by some obstruction above the larynx, especially in the mouth cavity.
Consonants Classification
- Place of Articulation (Consonant Sounds )
- Bilabial sounds are produced by two lips, they are : /p/, /b/, /m/, /w/.
- Labio- Dental sounds are produced in which the air is obstructed by the lower lip against the upper teeth. They are : /f/, and /v/.
- Dental Sounds are produced by the obstruction of the out going by the tip of the tongue and upper teeth.
The sounds are : /e/, and /ð/
- Alveolar Sounds are produced in which the air is obstructed by the tip of the blade of the tongue against the teeth ridge or gum.
The sounds are : /t/, /d/, /s/, /z/, and /l/.
- Post Alveolar sounds are produced by the tip of the tongue against behind the teeth ridge. The sounds is /r/.
- Palato Alveolar sounds are produced by the blade of the tongue with the teeth ridge and stimultaneously. The sounds are : /3/, /t∫/, /dЗ/ and /∫/.
- Palatal Sounds is produced by obstructing the air by raising the front part of the tongue against the hard palate. The sounds is : /∫/.
- Velar Sounds are produced by articulating the back of the tongue with the soft palate. The sounds are : /k/, /g/, and /η/.
- Glottal Sounds. The obstruction of the air is formed at the glottis that is by putting the vocal cords in close contact. The sounds is /h/.
- Place of Articulation (Consonant Sounds )
- Bilabial sounds are produced by two lips, they are : /p/, /b/, /m/, /w/.
- Labio- Dental sounds are produced in which the air is obstructed by the lower lip against the upper teeth. They are : /f/, and /v/.
- Dental Sounds are produced by the obstruction of the out going by the tip of the tongue and upper teeth.
The sounds are : /e/, and /ð/
- Alveolar Sounds are produced in which the air is obstructed by the tip of the blade of the tongue against the teeth ridge or gum.
The sounds are : /t/, /d/, /s/, /z/, and /l/.
- Post Alveolar sounds are produced by the tip of the tongue against behind the teeth ridge. The sounds is /r/.
- Palato Alveolar sounds are produced by the blade of the tongue with the teeth ridge and stimultaneously. The sounds are : /3/, /t∫/, /dЗ/ and /∫/.
- Palatal Sounds is produced by obstructing the air by raising the front part of the tongue against the hard palate. The sounds is : /∫/.
- Velar Sounds are produced by articulating the back of the tongue with the soft palate. The sounds are : /k/, /g/, and /η/.
- Glottal Sounds. The obstruction of the air is formed at the glottis that is by putting the vocal cords in close contact. The sounds is /h/.
- Manner of Production
- Plosive/ Stop Sounds. The out going air is completely blockage in the mouth passage by the two articulators while producing the sounds, then the air stream is suddenly released. So that the air s escapes with the explosives. The sounds are /p/, /b/, /t/, /d/, /k/, and /g/.
- Affricative Sounds. a complete closure at the some point in the mouth behind where the air pressure builds up. The sounds are /t∫/, and /dЗ/.
- Fricative. The out going air is partially obstructed. The two articulators are brought close to each other. So that there is a slight narrow opening left for the air to past out. the sounds are : /f/, /v/, /θ/, /ð/, /s/, /z/, /З/, and /h/.
- Nasal. The soft palate ulvula is lowered, so that there is a complete closure of the out going air in the mouth cavity; consequently the air stream is allowed go trough the nose passage. The sounds are : /m/, /n/, and /ŋ/.
- Lateral. A complete obstruction is made by putting the tip of the tongue against the teeth ridge. The air meets with a complete obstruction in the central of the mouth, it passes trough the both sides of the tongue. The nasal cavity is also closed by raising the soft palate. And divided into 2 The sounds are : /l/.
a) Rolled/Flapped. The tip of the tongue is made to vibrate against the teeth ridge, that is there is a rapid series of closing and opening of the air passage. The sounds are /r/.
b) Semi Vowel. The way of producing semi vowels is the same as that of producing vowels; they are both oral, central and resonant. But semi vowels function as non- syllabic sounds or consonants while vowel function as syllabic sounds. But is lacks of stress and its weak force makes more consonantal rather than vowel like. The sounds are : /j/, /w/
The Sounds in English and Their Representation
In English, there is no one-to-one relation between the system of writing and the system of pronunciation. The alphabet which we use to write English has 26 letters but in (Standard British) English there are approximately 44 speech sounds. The number of speech sounds in English varies from dialect to dialect, and any actual tally depends greatly on the interpretation of the researcher doing the counting. To represent the basic sound of spoken languages linguists use a set of phonetic symbols called the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). The chart below contains all of the IPA symbols used to represent the sounds of the English language. This is the standard set of phonemic symbols for English ( RP and Similar accents).
0 Response to "Consonant Sounds on English Speech"
Post a Comment